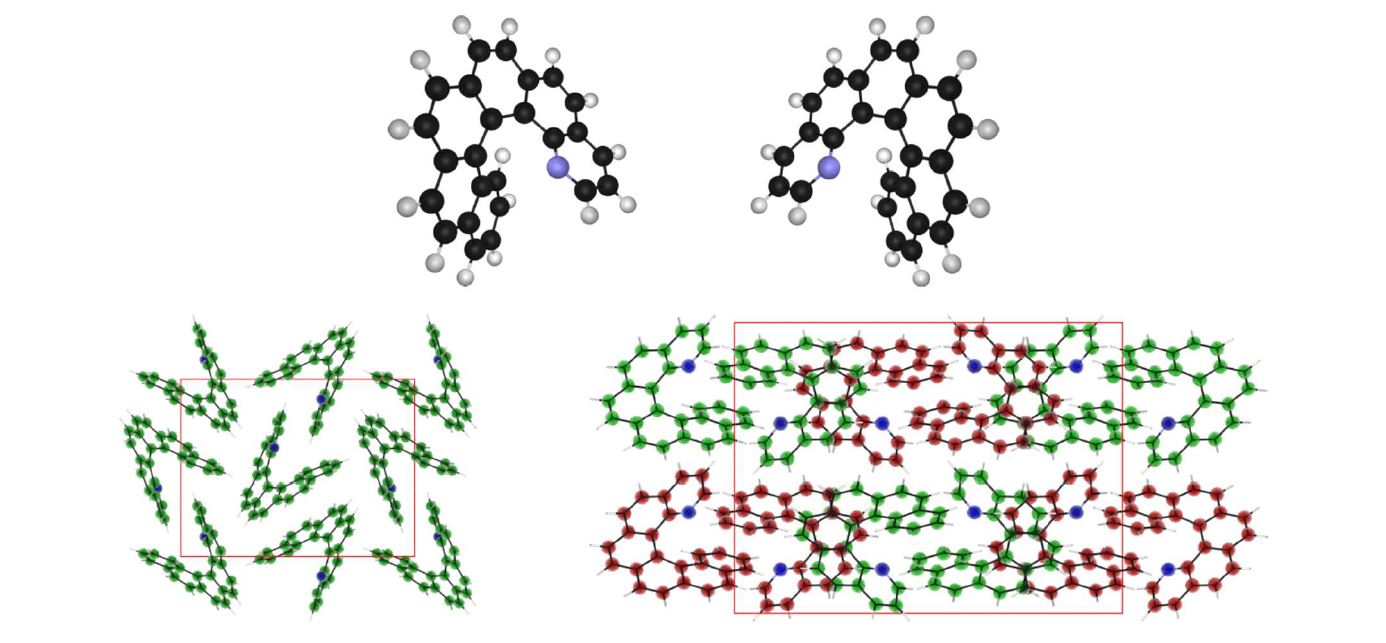
Conventional density functionals do not include the physics of London dispersion, which is necessary to model van der Waals interactions. The exchange-hole dipolemoment (XDM) model is a non-empirical density-functional approach to model dispersion, in which the atomic dispersion coefficients are dependent on the local chemical environment. XDM can be paired with popular base density functionals to obtain highly accurate results for both gas phase and solid-phase systems. In this talk, several applications of XDM are presented, including reaction kinetics, surface adsorption, metallophilicity, enantiomeric excess of chiral crystals, and acid-base co-crystals. A particular emphasis is placed on the problem of molecular crystal structure prediction.