Current Research Activities
Current research activities of the extreme load effect research group are in five main areas: blast load effects on reinforced concrete columns, blast hazard mitigation through vented suppressive shields, blast and impact load effects on steel anchors, and behaviour of ribbon floating bridges and impact load effects on vehicle bollards.
Blast load effects on reinforced concrete columns
 Terrorist attacks and accidental explosion effects on buildings have been steadily increasing in the past decades. Research to investigate the effects of explosion on the response of columns have concentrated on their response to far-field explosions. Extreme load effect research group is currently investigating the behaviour of reinforced concrete columns under near-field explosion effects. Both experimental testing of columns to live explosions and numerical simulations of the response of columns to near-field explosions is being investigated. Additionally, the effects of explosions and high strain-rates on the development length of steel reinforcement in reinforced concrete elements is also investigated.
Terrorist attacks and accidental explosion effects on buildings have been steadily increasing in the past decades. Research to investigate the effects of explosion on the response of columns have concentrated on their response to far-field explosions. Extreme load effect research group is currently investigating the behaviour of reinforced concrete columns under near-field explosion effects. Both experimental testing of columns to live explosions and numerical simulations of the response of columns to near-field explosions is being investigated. Additionally, the effects of explosions and high strain-rates on the development length of steel reinforcement in reinforced concrete elements is also investigated.
Blast hazard mitigation through vented suppressive shields
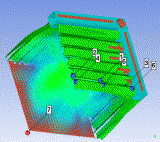 With ever increasing city boundaries, explosive plants originally sited outside populated areas are under pressure to evaluate the hazard they pose to proximate populations and traffic routes. Where this hazard is high, mitigation options available include acquiring more land around the plant to increase standoff distance or reducing the amount of explosives stored in the plant. Vented suppressive shield (VSS) containers are designed to attenuate the blast pressure outside the containers while eliminating fragment hazards from the exterior. VSS containers present a more economical option for explosive plants. Extreme load effects research group is investigating the efficiency of suppressive shield configuration in attenuating blast pressure and impulse in the surrounding environment and to reduce the required standoff distances for explosive plants and storage facilities.
With ever increasing city boundaries, explosive plants originally sited outside populated areas are under pressure to evaluate the hazard they pose to proximate populations and traffic routes. Where this hazard is high, mitigation options available include acquiring more land around the plant to increase standoff distance or reducing the amount of explosives stored in the plant. Vented suppressive shield (VSS) containers are designed to attenuate the blast pressure outside the containers while eliminating fragment hazards from the exterior. VSS containers present a more economical option for explosive plants. Extreme load effects research group is investigating the efficiency of suppressive shield configuration in attenuating blast pressure and impulse in the surrounding environment and to reduce the required standoff distances for explosive plants and storage facilities.
Behaviour of ribbon floating bridges
Ribbon floating bridges are temporary structures used in times of war or emergency to move troops and supplies across water bodies. Unlike conventional bridges, floating bridges use the buoyancy force exerted by the water to resist the imposed vehicular loads. Most ribbon floating bridges are designed, constructed, stock-piled, and deployed to the field when required. With increasing vehicular weights and speeds, floating bridges need to be evaluated to understand their behaviour under new loading and operational conditions. Researchers in the extreme loads effects research group conducted experimental and numerical investigation to study the behaviour of ribbon floating bridges under different loading conditions.
Steel anchor behaviour under blast and impact loading
Anchorages are often used to connect elements in critical infrastructure construction. For example, steel anchors are used to connect blast-resistant window frames to building structures. The behaviour of steel anchors under blast and impact loading, however, is not well researched. Reserachers in the extreme load effects research group are currently studying the effects of increased loading rates on the behaviour of cast-in and adhesive steel anchors using the finite element analysis method (LS-DYNA).