Hybrid testing is a testing technique that has been gaining popularity over the past decade to better understand the performance of large-scale civil engineering infrastructure under the effects of natural hazards (e.g. earthquakes, wind, blast, impact). Hybrid testing uses a numerical model of a structure in combination with a physical test setup in a laboratory to capture the overall response behaviour of a structure. In this configuration, elements in a building whose behaviour is either not well understood or difficult to model can be physically tested in the laboratory, while the remaining portions of a structure that behave in a predictable manner are modelled analytically. In doing so, hybrid simulation provides a cost-effective, realistic, and accurate structural testing method for understand ing the local behaviour of select structural elements and also capturing the global response of the entire structure.
The schematic below show a hybrid simulation example for a simple structure subject to an earthquake. In this configuration, a single column of the frame is tested in the lab, while the remaining column and beam are modelled analytically.
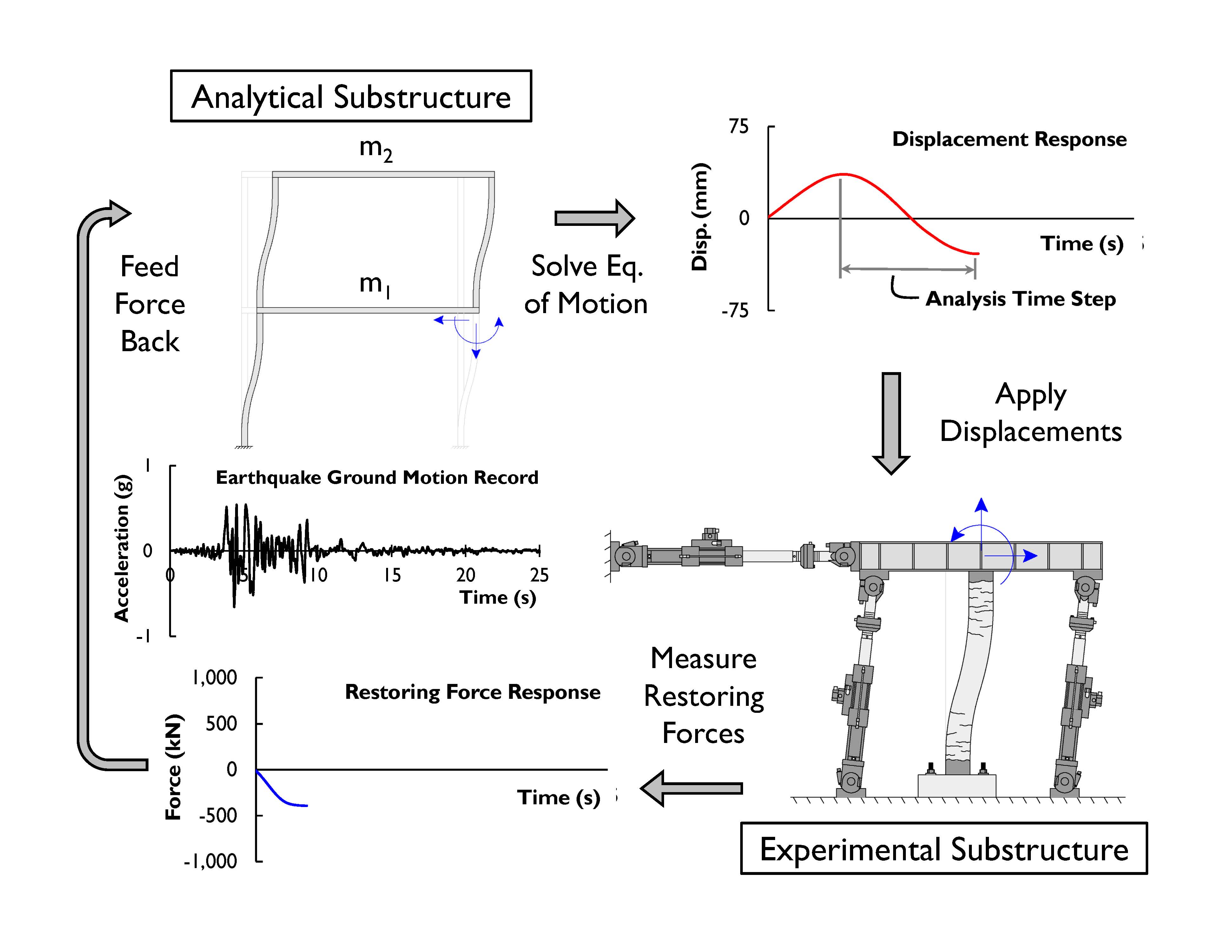
Example Hybrid Simulation of a 1-Storey Frame