The CABER Lab’s recent introduction to the research community at Carleton University has given the team the opportunity to develop new testing apparatus’. As the lab continues to grow, progress regarding testing development will be regularly updated on our website.
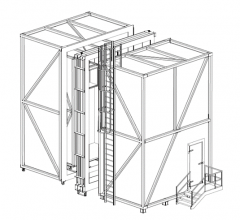
In partnership with CanmetENERGY Ottawa, additional testing facilities located in Bells Corners are currently under development. The new facility will house large scale testing apparatus’ which will preform the bulk of testing for the team moving forward.
Large Scale Equipment:
Guarded Hot Box
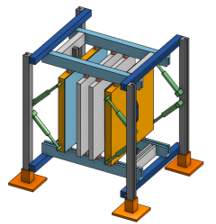
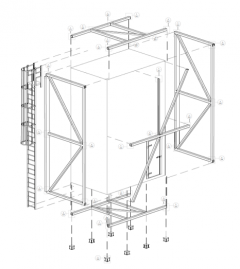
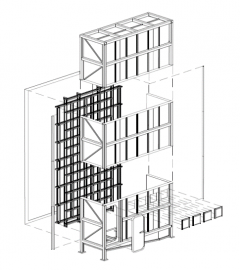
The Guarded Hot Box (GHB) will be the single largest piece of equipment in CABER and will be primarily used to accurately determine the overall effective thermal performance of complete wall assemblies. When complete, it will be one of the biggest guarded hot boxes in the world, capable of testing a sample area up to 3 m wide and 6 m tall. The climate side will be able to range from 55℃ to -35℃ for testing under all climate conditions, while the interior metering side can be controlled from 15℃ to 30℃.
On top of testing under standard conditions, transient conditions can be programmed in to the chambers control and different temperature cycles can also be tested. To determine the impact of air infiltration on thermal performance, both sides of the wall assembly can be individually pressurized up to 1000 Pa above atmospheric conditions.
Although primarily designed for thermal testing, hygrothermal testing can also be conducted in the GHB. To achieve this, humidity can be controlled when the chambers are above 4℃ between 10% and 95% relative humidity, while the chamber supports the installation of embedded relative humidity, temperature and moisture sensors to measure the movement of heat, air and moisture through and assembly. Finally, a 22 kW infrared heating system has been designed to simulate solar heating of the exterior façade, and will be used to evaluate the solar vapor drive in building envelope systems.
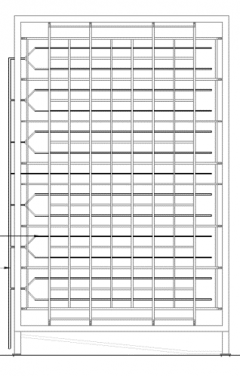
Pressurized Spray Rack (PSR)
This test apparatus will be designed interchangeably test wall assemblies with the guarded hot box, and will focus on measuring and observing air and water leakage of an assembly. A total of 96 nozzles can simulate up to 40 GPM of rain on a wall assembly and the test apparatus can be pressurized to 1000 Pa to test air sealing methods and measure air leakage. After testing, samples can be moved from the PSR to the GHB for thermal testing, freeze/thaw testing, or testing the impact of solar heating on wet samples to determine if inward vapour drive is present.
Meteorological Monitoring

To determine the conditions the building envelope is exposed to, a weather station has been installed at the future site of CABER in Bells Corners. This weather station focuses on measuring the solar conditions using a solar tracker to measure the indirect, direct and total horizontal radiation, as well as the incident radiation on a vertical surface in each of the four cardinal directions. The second focus is on measuring precipitation, with a heated rain gauge, and driving rain gauges in each of the four cardinal direction to determine the precipitation that strikes a surface. Finally, temperature, relative humidity, barometric pressure and wind conditions are measured and recorded. Long-term this data will be live streamed and accessible via a dedicated site, but in the mean-time, data is available by contacting Chris Baldwin or Brock Conley.
In-Situ Wall Openings
CABER will be built with six 3 m x 3 m openings (4 along the south façade, 2 along the west façade) which will accommodate long term in-situ testing of both heat and moisture transfer within the assemblies over multiple years. Each opening is wired to monitor up to 64 sensors which will be continuously monitored and the data recorded. Additionally, active systems integrated into the building envelope can be tested within the southern facing openings. Finally, 2 southern openings will be connected to 3 m by 3 m rooms on the inside of the facility, which will allow different and controlled interior conditions, as well as testing the impact of new building envelope designs on the building occupant’s comfort.
Material Property Testing:
In addition to the large scale test apparatuses being designed and built in CABER to test large building envelope assemblies, a full suite of small scale systems have been built/purchased for use within CABER, and are detailed below.
Guarded Hot Plate
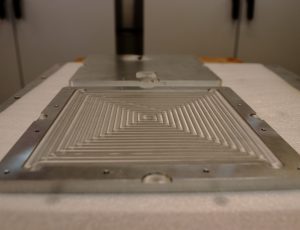
A guarded hot plate is used to accurately measure the thermal conductivity of a material sample. It consists of two chilled plates and a hot plate and the heat flow through the sample being tested. Currently, one unit is installed within CABER, with a metering area of 200 mm by 200 mm and cold plates down to -15℃, while the hot plates can reach temperature of 65℃. A second unit is being developed within the lab, with a metering area of 450 mm by 450 mm and capable of temperatures down to -35℃.
Heat Flow Meter
Used to measure the heat capacity of a material, CABER has built a heat flow meter using two hot plates, which will be preheated and then brought into contact with the sample material. The time required for the sample to increase in temperature allows the heat capacity to be measured.
Constant Temperature and Humidity Chambers
Two large constant temperature and humidity chambers have been installed within CABER and are used for two main purposes. The first is to artificially age materials at elevated temperature and humidity and when coupled with the guarded hot plates, the degradation in thermal performance can be determined. The second purpose is to determine the moisture permeance and conditioning of materials.
Data Acquisition
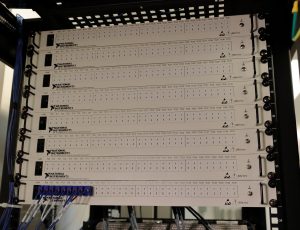
CABER and SESL have large data acquisition systems allowing for vast amounts of data to be collected in real time. Sensors and data collected can range from miniscule resistance measurements for temperature readings to large voltage readings for power consumed.