Wireless Network Personalization: Optimizing User Satisfaction with Predictive Analytics
|
| Overview |
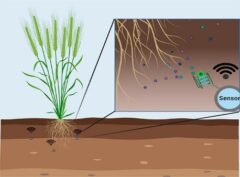
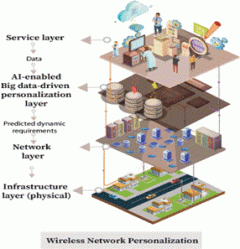
Current wireless networks are designed with a focus on worst-case scenarios across user applications, leading to over-engineering and inefficient resource use. This novel Wireless Network Personalization technology optimizes wireless networks in real-time, at the application and end-user layer. Using predictive analytics, big-data techniques and machine learning it effectively tailors performance to optimize individual user satisfaction and resource utilization.
Inventor(s): Rawan Alkurd, Halim Yanikomeroglu, and Ibrahim Abualhaol |
| Benefits |
- Resource Efficiency: Optimizes resources for critical applications like public safety and autonomous vehicles.
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: Delivers personalized service, improving user experience, retention, and acquisition.
- Operational Flexibility: Empowers operators to customize services and pricing, enhancing retention & attracting a diverse user base.
- Crisis Management: Prioritizes resource allocation for critical applications during emergencies.
|
| Applications |
- Telecom Operators
- Vendors and Manufacturers
- New Market Entrants to Wireless and Networking
- Big Data and Analytics Companies
|
| Status |
US 11,736,973B2 (issued Aug. 22, 2023)
CA 3,126,091 (filed Jul 27, 2021) |
| Seeking |
Development partners and licensees |
Development stage
|
Concept validated
|
Faster-Than-Nyquist Signaling Detector: Enabling data transmission beyond the classical limit
|
| Overview |
While the demand for high data transmission and bandwidth optimization is exponentially increasing, existing technology to enable data transmission beyond the classical limit are prohibitively complex. This Faster-than-Nyquist (FTN) signaling detector for ultra-high-order quadrature-amplitude modulation is capable of removing inter-symbol interference and reconstructing transmitted data symbols, within the same bandwidth and using the same transmission power as conventional Nyquist signaling.
Inventor(s): Ahmed Ibrahim, Ebrahim Bedeer, and Halim Yanikomeroglu |
| Benefits |
- Improved Spectral Efficiency: Increase of 7.5% – 58% in spectral efficiency compared to conventional techniques
- No Additional Bandwidth or Power: Ultra-high QAM data transmission without extra bandwidth or increased power.
- High Transmission Quality: Significantly lowers ISI and bit errors, maintaining high transmission quality.
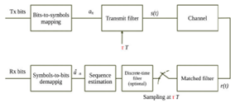
|
| Applications |
- Cellular Mobile Networks: ex. in high speed microwave point-to-point connections (ex. RAy3)
- Internet Service Providers: compatible with the DOCSIS 3.1 standard
- Digital Video Broadcasting: such as satellite digital video broadcasting (ex DVB-S2) or cable-based standards (ex. DVB-C2)
|
Status
|
US application 18/246,637 (international filing date Sept. 24, 2021)
CA application 3,196,718 (international filing date Sept. 24, 2021)
Available for licensing and/or development partnerships
|
| Seeking |
Development partners and licensees |
Development stage
|
Concept validation
|
DNA Aptamers to Detect and Prevent Neurodegenerative Diseases
|
| Overview |
Carleton researchers have developed novel DNA aptamer sequences that bind to alpha-synuclein monomers and inhibit formation of the larger oligomers and fibrils associated with the onset and progression of neurodegenerative disease such as Parkinson’s Disease. Data from studies in a mouse model of Parkinson’s Disease show that the DNA aptamers, when packaged in liposomes, can cross the blood-brain barrier and bind to alpha synuclein. Further, the DNA aptamers have been incorporated into a diagnostic device where they have been shown to detect low levels of alpha-synuclein in biological samples.
Inventor(s): Maria DeRosa, Matthew Holahan, Erin McConnell, Katelyn Ventura, Joshua Callahan, and Vernon Hunt |
| Benefits |
- Response: Compared with conventional antibodies, aptamers are not typically recognized by the immune system and are not immunogenic or toxic
- Strong Selectivity: Aptamers can discriminate between different conformations of the same target protein
- Synthesis & scalability: Can be easily generated by chemical synthesis
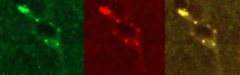
Aptamer delivery to the brain and binding to α synuclein in treated mice. Fluorescence microscopy images of the distribution of α-syn-1 aptamer and co-localization with α-synuclein in brain tissue of treated mice. Left: anti- α -synuclein antibody (green) Middle: labelled aptamer, delivered by targeting liposome (red). Right: Image overlay showing extensive co-localization |
| Applications |
- Diagnostic: point-of-care and laboratory methods to detect onset and monitor progression of neurodegenerative diseases
- Therapeutic: to reduce protein fibrillation and mitigate onset and progression of neurodegenerative diseases
|
| Status |
US patent 11,814,625 B2 (issued Nov. 14, 2023)
CA application 3,079,909 (filed Sept. 24, 2021) |
| Seeking |
Development and pre-clinical testing partners and/or licensees |
| Development stage |
Pre-clinical studies
|