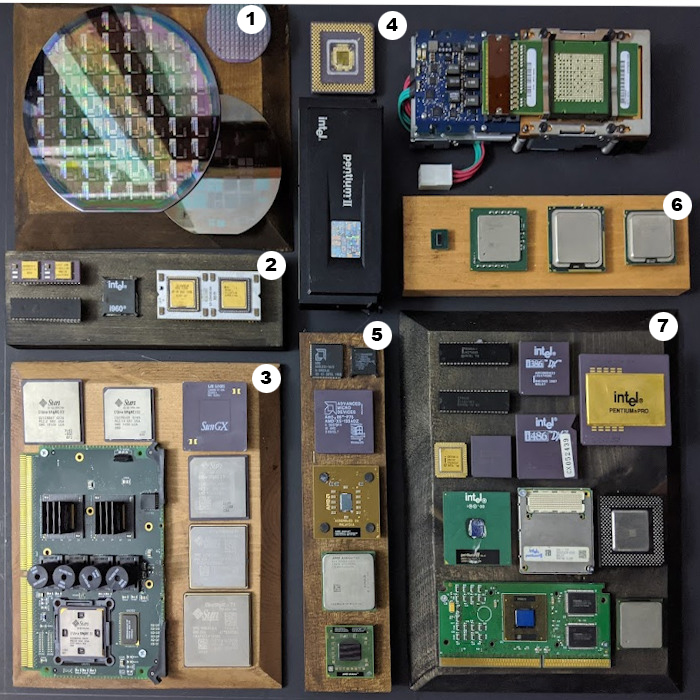
The above is an image map and you can click on the items for more information
- Silicon Wafers
- Specialty CPU’s
- SUN Microsystems CPU’s
- CPU Design
- AMD CPU’s
- Intel Xeon and Atom CPU’s
- Intel CPU’s
1. Silicon Wafers
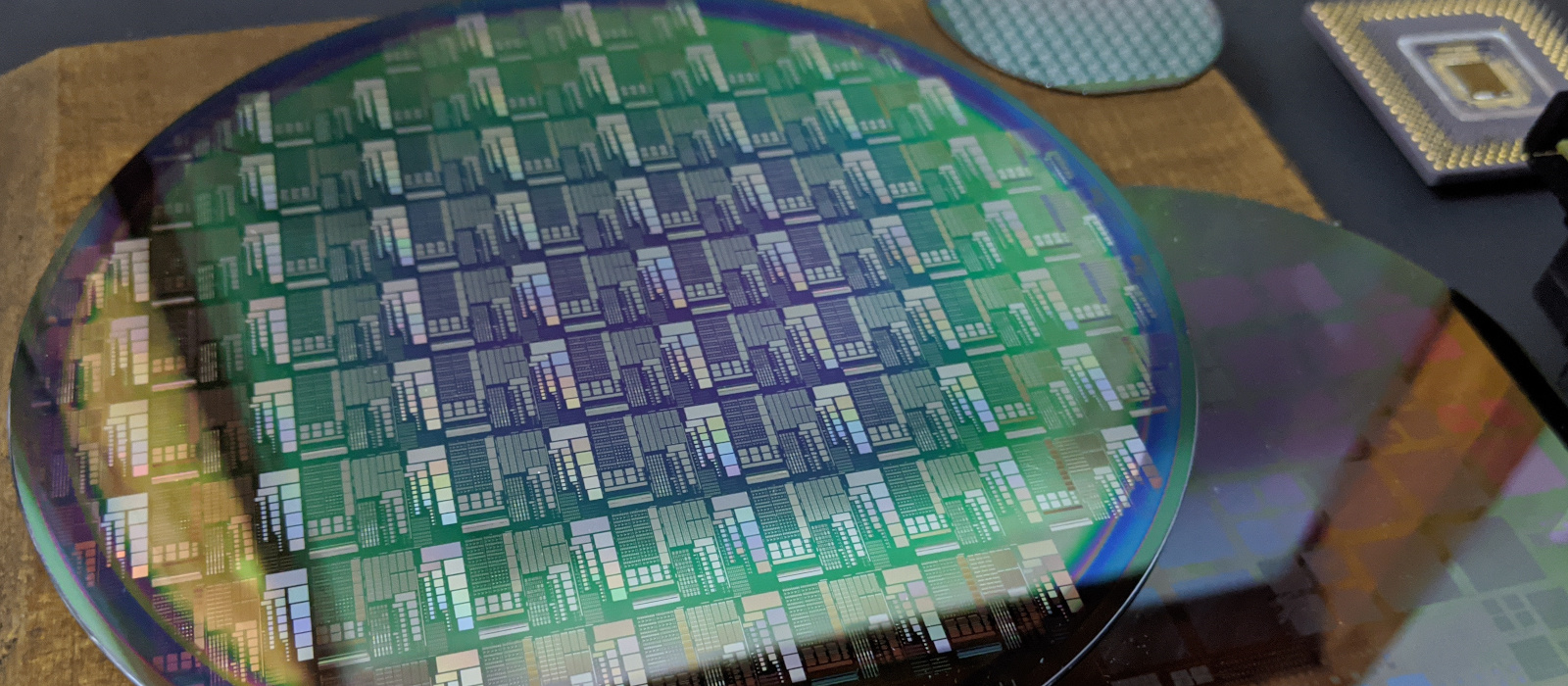
In this section, you can see a few circular silicon wafers. Silicon is a semiconducting metalloid used for diodes, transistors, and more. These are used in the fabrication of CPUs.
2. Specialty CPUs
We are accustomed to hearing about Intel, AMD and Arm but there are and were many other famous Microprocessor manufacturers!
DEC F11
Zilog Z80
DEC J-11
Intel i960
DEC F11

Year: 1979
Usage: PDP-11
Reference: http://www.cpu-collection.de/?l0=co&l1=DEC&l2=PDP-11
Description: The first item in the top left corner is the DEC F11 (code name: the Fonz). Released in 1979, the DEC F11 is a chipset famous for being used in the PDP-11, a 16-bit minicomputer series by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC).
DEC J-11

Year: 1983
Usage: PDP-11
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DEC_J-11
Description: This is the DEC J-11. Similar to the F11, the DEC J-11 is a chipset famous for being used in the PDP-11. Introduced in 1983, the J-11 was DEC’s last PDP-11 microprocessor design.
The PDP-11 were large fridge-sized computers and used a lot of power! Engineering had and abandoned one in their hallway and a student ‘borrowed’ it and never returned it! LoL.
Zilog Z80

Year: 1976
Usage: Many including Sega Genesis, Heathkit H89, Osborne 1, TRS-80 (“Trash-80”) Model 1-4, Many embedded systems used by Casio, Sharp and Epson.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zilog_Z80
Description: The Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor released in 1976 as Zilog’s first product. The Z80 is an extension and enhancement of the first 8-bit microprocessor, the Intel 8080.
In the 1980’s the infamous Radio Shack sold a very popular TRS-80 personal computer. It was so slow and clumsy many nicknamed it the Trash 80! The Trash 80 used the Zilog Z80 microprocessor!
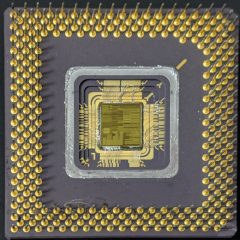
Intel i960

Intel i960 NG80960KB-25
Year: 1984-2007
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_i960
Description: The Intel i960 is a RISC-based microprocessor design that became popular during the early 1990s as an embedded microcontroller. This one is a plastic flat package and would have been embedded on a circuit board or motherboard. You can see the pins are bent where they were pulled from the circuit board.
3. SUN Microsystems CPUs
Sun SuperSPARC
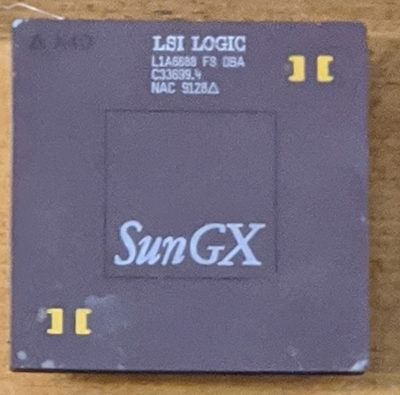
Year: 1992-1995
Usage: Sun SPARCStation 10/20
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SuperSPARC
Description: The Sun SuperSPARC is a single core microprocessor that implements the SPARC V8 instruction set architecture. In 1995, the CPU was replaced by the Sun UltraSPARC.
These SUN microprocessors were desktop computers and typically cost ~$10,000 in 1995. Accounting for inflation the cost is closer to ~$20,000 in 2022! They used proprietary CRT monitors, keyboard and mice! They were the School of Computer Science’s first generation mail, file and storage servers and doubled as desktop computers!
Sun UltraSPARC II
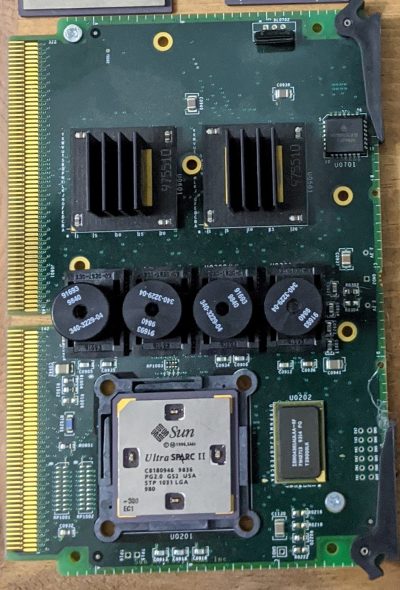

Year: 1997
Usage: Servers/Workstations
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UltraSPARC_II
Description: The Sun UltraSPARC II “Blackbird” is the second generation of Sun’s UltraSPARC series. It has one single core clocked at 250 MHz, eventually reaching 650 MHz in later variants. Some SUN CPU’s were mounted on interface cards.
Sun UltraSPARC IIi

Year: 1997
Usage: Servers/Workstations
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UltraSPARC_II
Description: The Sun UltraSPARC IIi “Sabre” is a more low cost version of the Sun UltraSPARC II that operated at 270 to 360 MHz.
Sun UltraSPARC III

Year: 2001-2004
Usage: Servers/Workstations
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UltraSPARC_III
Description: “The UltraSPARC III “Cheetah”, is a microprocessor that implements the 64-bit SPARC V9 instruction set architecture developed by Sun Microsystems and fabricated by Texas Instruments. It was introduced in 2001 and operates at 600 to 900 MHz.”
Sun UltraSPARC IV (and IV+)
Year: 2004/2005
Usage: Servers (Sun Fire V490, V890, E2900, E4900, E6900, E20K and E25K)
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UltraSPARC_IV
Description: The Sun UltraSPARC IV “Jaguar” is the successor to the UltraSPARC III. It implements the 64-bit SPARC V9 instruction set architecture and was also the first SPARC processor with multiple cores (2). The processor implements 2 modified UltraSPARC III cores.
Released in mid 2005, the UltraSPARC IV+ “Panther” is similar to the IV, having 2 cores. One main difference between the two is that the UltraSPARC IV+ uses 90 nanometer technology Instead of the 130 nanometer manufacturing process of the UltraSPARC IV.
Sun UltraSPARC T1
Year: 2005
Usage: Servers/Workstations
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UltraSPARC_T1
Description: The Sun UltraSPARC T1 “Niagra” is a multithreading and multicore CPU designed to lower the power usage of servers. The UltraSPARC T1 was Sun’s first CPU that was both multicore and multithreaded. “The processor is available with four, six or eight CPU cores.”
4. CPU Design
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Die_(integrated_circuit)
Description: This is a Pentium CPU with an exposed CPU die. Close up photo of the Pentium CPU die
Intel Itanium

Year: June 2001 – July 2021
Usage: Enterprise servers, high-performance computing systems
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Itanium
Description: The Intel Itanium is a family of CPUs that implemented the IA-64 architecture. HP partnered with Intel to develop the architecture and processor. It was planned to release in 1998 but after delays and many big companies cancelling their plans to support the processor, it was given the nickname “Itanic” in the media as a reference to the Titanic.
HP wanted a share of the enterprise server market and sold servers with 8 Itanium processors. These systems at the time would cost $200,000 each!
5. AMD CPUs
AMD Am286

AMD M80L286-16/S
Year: 1984
Usage: Personal computers
Reference: https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/amd/am286
Description: The AMD Am286 is a processor designed by Intel and manufactured by AMD. The Am286 is identical to Intel’s 80286.
AMD Am386

Year: 1991
Usage: Personal computers, workstations
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Am386
Description: The AMD Am386 is a reverse engineered clone of Intel’s i386 processor. Before, AMD was a second source for x86 CPUs but this release made AMD a legitimate competitor to Intel.
AMD Am5x86

AMD-X5-133ADW
Year: 1995
Usage: Personal computers, embedded systems
Reference: https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/amd/am5x86
Description: The AMD Am5x86 is a family of 486 based CPUs. The Am5x86 processors were higher clocked than the other 486 based processors but also lower priced. “This family solidified AMD’s position as the official Intel competition.”
AMD Athlon
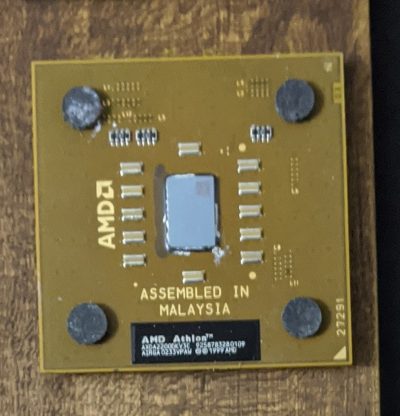

AMD Athlon XP 2200+
Year: June 1999
Usage: Personal computers
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Athlon
Description: The AMD Athlon was released as AMD’s high end processor brand. The CPU was the first 7th generation x86 processor. The Athlon was also the first desktop processor to reach speeds of 1GHz.
AMD Athlon 64

Year: September 2003
Usage: Personal computers
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Athlon_64
Description: The AMD Athlon 64 is the 3rd CPU in the Athlon line. The Athlon 64 was the first 64-bit processor targeted at the average consumer and AMD’s second AMD64 architecture CPU.
AMD Athlon 64 X2

Year: May 2005
Usage: Personal computers
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Athlon_64_X2
Description: The AMD Athlon 64 X2 was AMD’s first native dual core desktop CPU.
6. Intel Xeon and Atom CPUs
Intel Atom
Year: 2008-Present
Usage: Netbooks, mobile devices
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_Atom
Description: The Atom is the name of Intel’s line of ultra low voltage CPUs. The main goal of these processors was to reduce power consumption.
Intel Xeon

From left to right: Xeon 80532, Xeon E5502, Xeon E5335
Year: 1998-Present
Usage: Servers/Workstations
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xeon
Description: The Xeon is Intel’s non-consumer based microprocessor line. “Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for ECC memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and more”
7. Intel CPUs
Intel 8080

Intel P8080A-1
Year: April 1974
Usage: Altair 8800 Computer, Processor Technology SOL-20 Terminal Computer
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_8080
Description: The Intel 8080 is Intel’s second 8-bit CPU. The initial specified clock rate of the processor was 2 MHz. Some common variants of the processor are the 8080A-1 (shown above) and the 8080A-2. These variants are clocked higher than the original at 3.125 MHz and 2.63 MHz respectively.
Intel 8088

Year: June 1979
Usage: IBM PC,
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_8088
Description: The Intel 8088 is a variant of the Intel 8086 with an 8-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The execution unit of the 8088 is identical to that of the 8086, only the data bus is 8-bit instead of 16. The max clock rate of the processor was 5mhz to 16mhz depending on the variant.
Intel 80186

Year: 1982
Usage: IBM PC/AT, the Dulmont Magnum laptop, the “Mindset”, the Siemens PC-D, the HP 100LX, and many more
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_80186
Description: The Intel 80186 (aka. iAPX 186, or 186) is a microprocessor and microcontroller based off of the Intel 8086. “It had a 16-bit external data bus multiplexed with a 20-bit address bus.” The initial clock rate of the 80186 was 6 MHz. This pretty CPU had contacts and not pins, the design proved to be ahead of its time!
Intel 80286

Year: February 1982
Usage: IBM PC/AT
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_80286
Description: The Intel 80286 (aka. iAPX 286, or 286) is a 16-bit microprocessor based off of the Intel 8086 with max clock rates ranging from 5 to 25MHz depending on the variant. “It was the first 8086-based CPU with separate, non-multiplexed address and data buses and also the first with memory management and wide protection abilities.”
Intel i386

Year: October 1985
Usage: High-end personal computers (including the Compaq Deskpro) and workstations.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I386
Description: The Intel 80386 (later renamed to the i386) is a 32-bit microprocessor that uses the 32-bit extension of the 80286 architecture. It has max clock rates ranging from 12 to 40MHz depending on the variant.
Intel i486

i486 DX CPU with a chunk chipped off the side of the ceramic top. Likely chipped because the thermal paste hardened and then prying it from the motherboard chipped it!
Year: April 1989
Usage:
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I486
Description: The Intel i486 (aka 80486) is a 32-bit microprocessor with max clock rates ranging from 16 to 50MHz depending on the variant. The i486 is the higher-performace successor to the i386.
Intel Pentium
Year: March 1993
Usage: Personal computers, servers, workstations
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pentium_(original)
Description: The Intel Pentium is the successor the i486. “It was instruction set compatible with the 80486 but was a new and very different microarchitecture design.” The microarchitecture was called P5, sine the processor was the 5th generation of 8086 the compatible CPUs. The Pentium has max clock rates ranging from 60 to 300MHz depending on the variant.
Intel Pentium Pro

Gold refining yields of the Pentium Pro have been reported to be as high as around . 33 grams per CPU!
Year: November 1995
Usage: Servers, high end desktops (Notably used in the ASCI Red Supercomputer)
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pentium_Pro
Description: The Intel Pentium Pro is an x86 CPU and is the successor the original Pentium. The Pentium Pro introduced the P6 microarchitecture. The Pentium Pro has max clock rates ranging from 150 to 200MHz depending on the variant.
Intel Pentium II

Year: May 1997
Usage: Workstations, servers, personal computers
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pentium_II
Description: The Intel Pentium II is an x86 CPU that includes an improved version of the Pentium Pro’s P6 core. It has max clock rates of 233 MHz to 450 MHz depending on the variant. This unique CPU was the mobile/laptop version.
Intel Pentium III
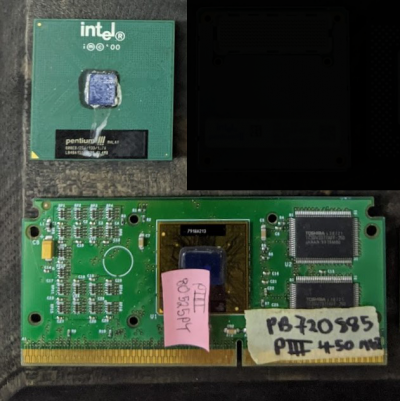

Above: Pentium III Mobile Below: Pentium III Desktop
Year: February 1999
Usage: Desktop and mobile computers
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pentium_III
Description: The Intel Pentium III is a 32-bit x86 CPU and is the successor to the Pentium II. The initial Pentium III CPUs were very similar to the Pentium II with few notable differences, the most notable being the SSE Instruction set. This one usually has a black plastic case with fan attached to it like its predecessor the Pentium II.
Intel Pentium 4
Year: November 2000
Usage: Desktops, Laptops, Servers
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pentium_4
Description: The Intel Pentium 4 is a 32-bit x86 CPU and is the successor to the Pentium III. These processors are based on the NetBurst (P86) microarchitecture. Later versions of the CPU introduced Hyper-Threading Technology.
Intel Celeron

Year: April 1998
Usage: Desktops, Laptops
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Celeron
Description: The Intel Celeron is the name of Intel’s lower-end IA-32 and x86-64 CPUs. They are targeted towards low-cost personal computers.