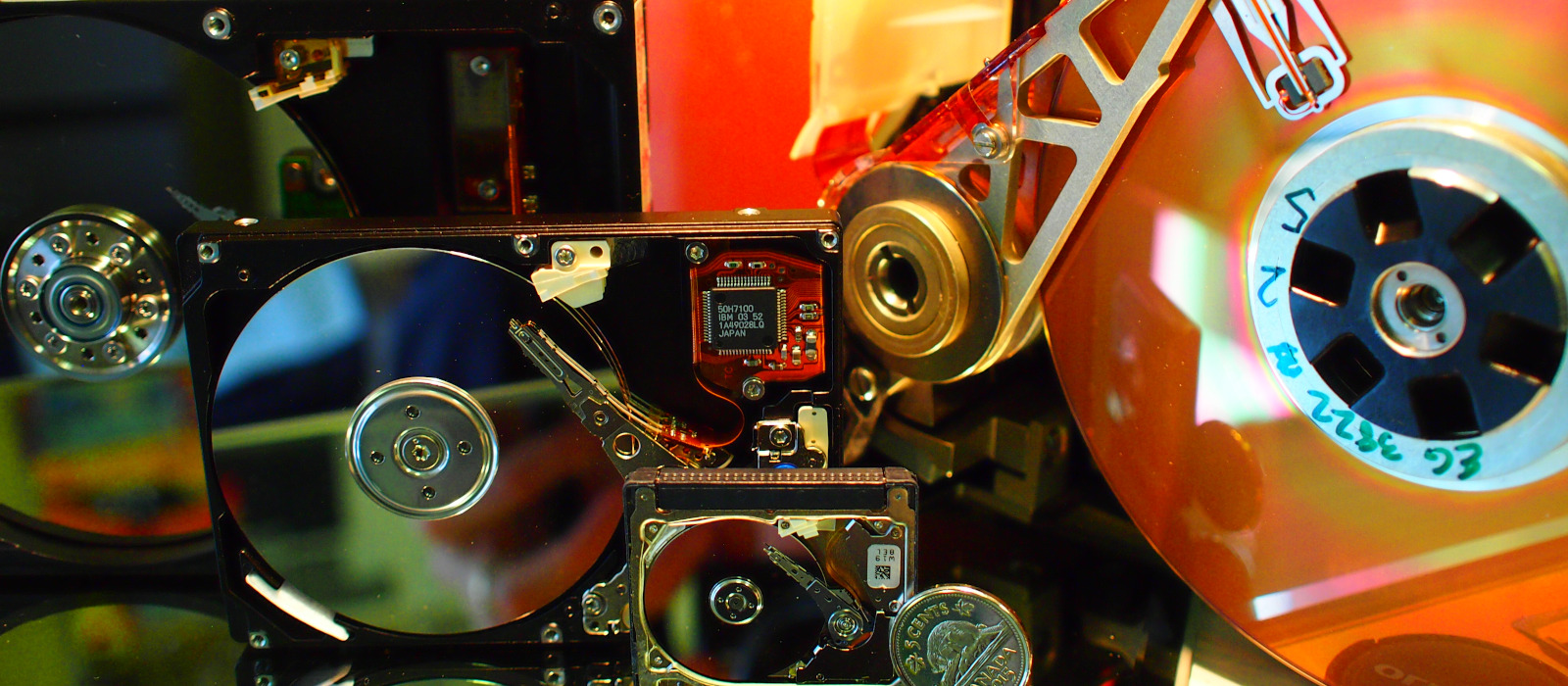
The above is an image map and you can click on the items for more information
Hard Drive Components
Hard Drive Form Factors
Hard Drive History: Notable Drives
Hard Disk Drive Interfaces
Improvement of Hard Drive Characteristics Over Time
Hard Drive Components
A hard disk drive (HDD) is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage and one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material.
Some key components of the hard drive are:
- An HDD has a spindle motor that spins the disks. This defines the rotational platter speed measured in rpm.
- An HDD has an actuator (motor) that positions the read/write head assembly across the spinning disks. This will read or write data to the disks.
- HDDs are connected to systems by standard interface cables such as PATA (Parallel ATA), SATA (Serial ATA), USB or SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) cables. This connects the drive to the computers motherboard or interface card.
- A hard drive’s Printed Circuit Board (PCB) connects various components that allow the hard drive to function. If you have ever handled a hard drive, you may recognize the PCB as the green or blue board on the bottom of the device.
IBM 0667 5¼ Inch Hard Disk Drive
On display are the main hard drive components. The PCB was removed as well as the hard drive cover exposing the read/write head and spinning disks.

Year: 1986
Capacity: 70 MB
Interface: EIDE
Platter Size: 5.25″
Description: This drive was in a production server at the School of Computer Science in 1990.
Hard Drive Form Factors
14 Inch Hard Disk Platter Size
Hard drive platters in a caddy. They can be dropped into the drive manually and then accessed via the mainframe.
Year: 1961
Description: This 14 inch 200 MB hard disk platter was used at Carleton Universities Computing Services (CCS) Honeywell CP-6 computer system which was in production from 1979-2005.

Vintage hard drive ad
Hard Drive History: Notable Drives
Hard drives have been engineered with spin rates as low as 1200 RPM and as high as 15K RPM. In 2022 most common RPM rates, in both laptop and desktop PCs, are between 5400 and 7200 RPM. The most common form factors for HDDs in enterprise systems in 2022 are 2.5-inch, also known as small form factor (SFF), and 3.5-inch, also known as large form factor (LFF).
| Name | Year | Capacity | Platter Size | Platter Rotation | Access Time | Weight | Interface | Description |
| IBM 350 | 1956 | 3.75 MB | 24″ | 1,200 RPM | 600 ms | 910 kg | — | The first disk drive |
| Seagate ST506 | 1980 | 5 MB | 5.25″ | 3,600 RPM | 85 ms | 2.1 kg | – | First 5¼-inch hard drive |
| Miniscribe 8425S | 1984 | 20 MB | 3.5″ | 3,600 RPM | 68 ms | 0.80 kg | XT | Early 3.5″ hard drive |
| Seagate Barracuda ST136475LW | 1992 | 36 GB | 3.5″ | 7,200 RPM | 7.6 ms | – | SCSI-2/3 | First 7,200 RPM drive |
| Seagate Cheetah ST37340SLC | 1996 | 97 GB | 3.5″ | 10,000 RPM | 2.99 ms | – | Ultra3 SCSI | First 10,000 RPM drive |
| Hitachi Deskstar 7K1000 | 2007 | 1 TB | 3.5″ | 7,200 RPM | 8.5 ms | SATA 3Gb/s | First 1 TB 3.5″ hard drive | |
| Western Digital Ultrastar He10 | 2014 | 10 TB | 3.5″ | 7,200 RPM | 8.0 ms | 0.66 kg | SATA | First 10 TB hard drive (Helium filled drive) |
The IBM 350 disk storage unit, the first disk drive, was announced by IBM as a component of the IBM 305 RAMAC computer system on September 13, 1956. The RAMAC program is generally considered to be the fundamental patent for disk drives.
An IBM 350 Hard Drive being transported
Hard Disk Drive Interfaces
SCSI: Small Computer System Interface
IDE: Integrated drive Electronics
FC: Fibre Channel
SAS: Serial Attached SCSI
SATA: Serial ATA
Improvements of Hard Drive Characteristics Over Time
| Parameter | IBM 350 | Developed to | Improvement |
| Capacity | 3.75 MB | 20 TB | 5,333,333:1 |
| Physical Volume | 1.9 m³ | 56,000:1 | |
| Weight | 910kg | 62g | 1500:1 |
| Avg. Access Time | 600ms | a few milliseconds | ~200:1 |
| Price | ~$30,000 (2020 dollars) | 300,000,000:1 | |
| Areal Density | 2,000 Bits/Inch² | 400,000,000:1 |